Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the C else if clauses in the if statement to execute a code block based on multiple conditions.
Introduction to the c else if clauses
The if statement allows to execute a code block when a condition is true.
The if...else provides you with an else clause to execute another code block when the condition is false.
Both if and if...else statements execute a code block based on a result of a single condition.
Sometimes, you want to execute code blocks based on multiple conditions. In this case, you need to use the else if clauses in the if statement.
The following shows the syntax of the if statement with an else if clause:
if(expression1)
{
// statement1
}
else if (expression2)
{
// statement2
}
else
{
// else-statement
}Code language: C++ (cpp)In this syntax, the if statement have two conditions: expression1 and expression2.
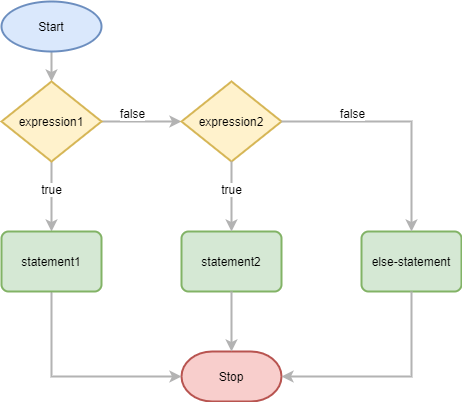
First, the if statement will execute the statement1 if the expression1 does not equal zero (or true).
If the expression1 is zero (or false), then the if statement executes the statement2 if the expression2 does not equal zero (or true).
If the expression2 equals zero (or false), then the if statement executes the else-statement in the else clause.
Note that the else clause is optional. If you don’t specify the else clause and both expression1 and expression2 are zero (or false), then the if statement doesn’t execute any statement.
Also, you can have multiple else if clauses in a single if statement. Each else if clause has its own condition.
Once a condition in the if or else if clause is true (not zero), the if statement stops evaluating the following conditions. For example, if the expression1 is true (not zero), the if statement won’t evaluate the expression2.
The following flowchart illustrates how the if...else if...else statement works:
C else if clause example
The following example uses the else if clause to determine the discount of a ticket based on an input age:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int age = 10;
// prompt for an age
printf("Enter your age:");
scanf("%d", &age);
// determine discount
float discount;
if (age <= 5)
{
discount = 1;
}
else if (age > 5 && age <= 12)
{
discount = 0.25;
}
else
{
discount = 0.1;
}
// calculate ticket price
float ticket_price = 100;
ticket_price = ticket_price * (1 - discount);
// display the ticket price
if (ticket_price == 0)
{
printf("You get a free ticket!");
}
else
{
printf("The ticket price is $%3.2f", ticket_price);
}
return 0;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)How it works.
First, the program prompts for enter an age:
printf("Enter your age:");
scanf("%d", &age);Code language: C++ (cpp)The age variable holds the input value.
Second, use an if...elseif...else clause to determine the discount.
If the age is less than or equal 5, the discount is 100%. If the age is from 6 to 12, the discount is 25%. Otherwise, the discount is 10%.
Third, calcualte the final ticket price based on the ticket price and discount:
float ticket_price = 100;
ticket_price = ticket_price * (1 - discount);Code language: C++ (cpp)Finally, display the ticket price:
// display the ticket price
if (ticket_price == 0)
{
printf("You get a free ticket!");
}
else
{
printf("The ticket price is $%3.2f", ticket_price);
}Code language: C++ (cpp)If the ticket price is zero, show that the ticket is free. Otherwise, display the ticket price.
Summary
- Use the
C else ifclauses in the if statement to execute code blocks based on multiple conditions.