Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn about a new type called C union and how to use it effectively in your program.
What is a C union? #
A structure allows you to define a new data type with multiple related fields. Each field takes up a separate storage location. For example:
struct point
{
int x;
int y;
};Code language: C++ (cpp)The point structure has two fields x-coordinate and y-coordinate. Each takes up a separate space in the memory.
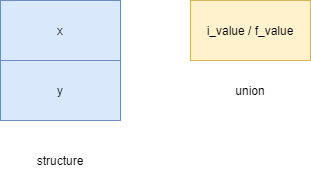
A union is similar to a structure. However, it defines a single location to store values of different fields at a single point in time.
union quantity {
int i_value;
float f_value;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)In this quantity union, the i_value and f_value fields share the same memory location.
The following picture illustrates the difference between a structure and a union:
By definition, a union is a type that stores different values in the same memory location but not simultaneously. It is a group of data objects that share a single block of memory.
C union syntax #
The syntax of defining a union is similar to the syntax of defining a structure type. The following illustrates the syntax for defining a union:
union union_name
{
type field_name;
type field_name;
//...
};Code language: C++ (cpp)In this syntax:
- First, start with the
unionkeyword followed by the union name. - Second, specify the fields with types.
To access a member of a union, you use the ( .) operator like this:
union_name.fieldCode language: C++ (cpp)Union vs. Structure #
In a structure, each field stores data separately. If you change the value of one field of a structure, the values of the other fields do not change.
However, all the fields share the same memory block in a union. This memory block is big enough to store the value of the largest field. Smaller members use as much memory as necessary. If you change a field’s value, other fields’ values also change.
If you need to store data in members simultaneously, use a structure.
Initialize a union #
C allows you to initialize a union in two ways:
- Initialize a union by initializing the first member of a union.
- Or initialize a union by assigning it to another union with the same type.
The following program demonstrates how to initialize a union in both ways.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
typedef union
{
char ch;
int flag;
float f;
} data;
data d;
d.ch = 'A';
// initialize one union to another
data d2 = d;
// initialize first member of union
data d3 = {'B'};
return 0;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)C Union Example #
In this example, we have an account structure that could be personal or business account based on the account_type enumeration. If it is a personal account the info member is associated with the person structure, otherwise, it is associated with the company structure:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// define account type: personal or business
enum account_type
{
personal = 1,
business = 2
};
// person name
struct person
{
char *name;
};
// company with name and tax no
struct company
{
char *name;
char *tax_no;
};
// profile
typedef union
{
struct person individual;
struct company biz;
} profile;
// account
typedef struct
{
char *username;
char *password;
enum account_type type;
profile info;
} account;
void display(account acc);
int main()
{
printf("Union Demo\n");
account acc1, acc2;
acc1.type = personal;
acc1.username = "acc1";
acc1.password = "secret";
acc1.info.individual.name = "John Doe";
display(acc1);
acc2.type = business;
acc2.username = "acc2";
acc2.password = "secret2";
acc2.info.biz.name = "My Company";
acc2.info.biz.tax_no = "112121";
display(acc2);
return 0;
}
/*
displays account on the screen
*/
void display(account acc)
{
switch (acc.type)
{
case personal:
printf("Personal Account\n");
printf("Username:%s\nName:%s\n", acc.username,
acc.info.individual.name);
break;
case business:
printf("Business Account\n");
printf("Username:%s\nCompany:%s\nTax no.:%s\n", acc.username,
acc.info.biz.name,
acc.info.biz.tax_no);
break;
}
printf("-------------------------------\n");
}Code language: C++ (cpp)In this tutorial, you have learned how to use a C union and understand the differences between a union and a structure.